Heart Attack
Heart Attack
Heart lies in the centre of the chest, slightly to the left. It beats almost 1 lakh times a day. It pumps blood in the body with each beat of the heart. This goes on 60-90 times a minute. For proper functioning of the heart, the myocardium has to be healthy.
The heart gets its nutrition and oxygen through blood that is supplied by coronary arteries. The heart is divided into two parts, right and left. The right heart has two chambers, right atrium and right ventricle. Similarly left side heart has two chambers - left atrium and left ventricle. In all, there are four chambers in the heart. The right side of the heart receives impure blood from the body and pumps it into the lungs. Blood gets purified in the lungs and returns back to the left side of heart from where it is pumped back into the body. Four valves, two on left side (mitral and aortic) and two on the right side of the heart (pulmonary and tricuspid) act as one-way doors to direct blood flow.
What is a heart attack?
The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood to various parts of the body. The heart receives oxygen rich blood through blood vessels called the coronary arteries. If these blood vessels become blocked, then the muscle of the heart does not get its supply of blood and dies. This is called a heart attack. The seriousness of the heart attack depends on the extent of damage to the heart muscle. The dead muscle may adversely affect the functioning of the heart by weakening the pumping effect, leading to (congestive heart failure), a condition which results in breathlessness and sweating of the feet.
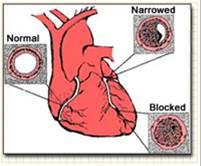
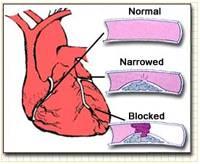
Why does it occur?
As we grow older, cholesterol deposits inside the blood vessels in various parts of the body, including the coronary arteries, causing gradual blockage of blood flow. This gradual narrowing is called atherosclerosis.
Men are more likely to have a heart attack than women. The women are protected possibly by the influence of the female sex hormones, oestrogen and progesterone. This protective influence stay at least till menopause.
Asians, including Indians appear to be at a higher risk of developing a heart attack.
The risk factors include:
- Cigarette smoking
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Overweight
- High cholesterol, and lower values of
HDL v the good cholesterol
- Lack of physical activity
- A family history of heart attacks
- Stress, chronic anger and anxiety
- Hereditary factors
What are the symptoms?
The signs may be difficult to identify and may mimic other conditions. Typically there is pain in the chest with tightness and difficulty in breathing. Sweating, nausea and feeling faint may be other symptoms. The pain may be in the front of the chest or behind the breastbone. From there it may go to the neck or left arm. Other symptoms like, vomiting, anxiety, cough, palpitation, , pain usually last longer than 20minutes . In severe cases, the patient may look pale due to a fall in blood pressure rapidly leading to death.
How is it diagnosed?
The doctor takes a detiled medical history, checks the heartbeat and records the blood pressure. An electrocardiogram, ECG, is taken which is record of the electrical activity of the heart. An ECG gives information about the rate at which the heart is beating, whether there are any abnormal rhythm patterns and also if there are areas of the heart muscle that are damaged due to the heart attack. It is important to remember that a normal ECG in the early stages does not exclude the possibility of a heart attack. Blood tests useful in identifying if the heart muscle has been damaged. An X-Ray of the chest may be done. An echocardiogram is a type of scan that gives useful information on the functioning of the heart. Conclusive evidence of blockage in the coronary vessels is provided by the coronary angiogram.
What first aid should be given to a patient during an attack?
Prompt treatment of heart attacks can save lives. Till expert medical help arrives, the patient must be made to lie down and all tight clothing loosened. If an oxygen cylinder is available, the patient must be given oxygen. If nitroglycerine or sorbitrate tablets are available, one or two tablets may be put under the tongue. Aspirin should also be given in a soluble form.
What is the treatment?
Heart attacks require immediate medical attention and hospitalisation. The first few minutes and hours are critical. In the early stages, medicines can be given to dissolve the clot in the coronary arteries. The heart rhythm is monitored and abnormal rhythms are promptly treated. Pain relieving medicines are given and the patient is encouraged to rest and sleep. If the blood pressure is high, drugs are given to lower the pressure.
The exact treatment is individualised and depends on the patient’s age and the severity of attack, the extent of damage to the heart and the extent of blockage in the vessels. Many times a more definitive procedure to remove the blockage may be necessary. This may be in the form of coronary angioplasty, dilatation of vessels using a balloon, or coronary bypass surgery.
How can heart attacks be prevented?
Those at high risk of developing heart attacks must take the following preventive measures:
'CHANGE IN LIFE STYLE'
- Their diet must be healthy and low in fats and salt, high in fibre and complex carbohydrates.
- Weight reduction is necessary for those who are over weight
- Physical exercise must be done regularly.
- Smoking must be stopped completely.
Those with diabetes, high blood pressure or high cholesterol must take regular drugs to keep their condition under control.
Source : Doctor - NDTV- Knowledge Portal
अंतिम सुधारित : 8/7/2020
Dr Devi Shetty, Heart Specialist, Narayana Hrudaya...
Causes for cardiovascular diseases, types, symptom...
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has launched...
This topic deals with information related to Blood...
